LoRa Network
LoRa™ is a low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technology enabling long-range, energy-efficient wireless communication over ISM radio bands. It supports secure two-way data transmission, making it ideal for IoT applications and smart city solutions.
LoRa™ technology utilizes Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) modulation, where signals are transmitted as frequency-varying chirps. This enhances range and improves signal resilience in challenging environments, such as urban and rural areas.
LoRa™ devices, or nodes, communicate with gateways that act as intermediaries between end devices and the internet. These gateways collect data from devices and transmit it to the network server for processing and analysis.
LoRa™ Network vs. Cellular Network
The primary difference between LoRa™ networks and cellular networks lies in their purpose and design. Cellular networks focus on high-speed, high-bandwidth communication over shorter distances, making them ideal for data-intensive tasks like video streaming and web browsing.
In contrast, LoRa™ networks are optimized for low-power, long-range communication, enabling efficient transmission of small data packets over vast distances at a lower cost, making them ideal for IoT applications.
Where is LoRa™ Network Used?
LoRa™ networks are leveraged across various industries to take advantage of long-range, low-power communication. Key sectors benefiting from this technology include:
Smart Agriculture: LoRa™ networks allow farmers to remotely monitor soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health, optimizing irrigation and boosting crop yields.
Smart Cities: By integrating LoRa™ sensors, cities can collect data on air quality, waste management, and parking, leading to enhanced efficiency and improved quality of life for residents.
Asset Tracking: LoRa™ networks enable real-time tracking of assets such as vehicles, containers, and equipment, helping businesses improve supply chain management and prevent theft.
A LoRa receiver operates in sub-GHz ISM bands, such as 868 MHz (EU), 915 MHz (US), and 470-510 MHz (China), using Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) modulation for long-range, low-power communication. It supports bandwidths of 125 kHz, 250 kHz, and 500 kHz, with spreading factors (SF7-SF12) that balance range and data rate. The receiver can detect weak signals down to -137 dBm, achieving communication ranges of 2-5 km in urban areas and up to 15 km in rural areas. With a maximum link budget of 168 dB and data rates between 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps, it ensures reliable connectivity. Power consumption remains low, with active mode drawing 10-20 mA and sleep mode as low as 1 µA, making it ideal for battery-powered IoT applications.
Benefits & Challenges of LoRa™ Technology
Benefits
- Long Range: LoRa™ networks provide coverage of several kilometers in urban areas and over tens of kilometers in rural environments.
- Low Power Consumption: LoRa™ devices are energy-efficient, allowing battery-powered operation for extended periods.
- Cost-Effective: With minimal infrastructure and maintenance costs, LoRa™ is a budget-friendly solution for IoT applications.
Challenges
- Limited Bandwidth: LoRa™ is optimized for small data transmissions, making it unsuitable for high-bandwidth applications like video streaming.
- Network Density: Proper gateway distribution is essential to ensure optimal coverage and performance across a LoRa™ network.
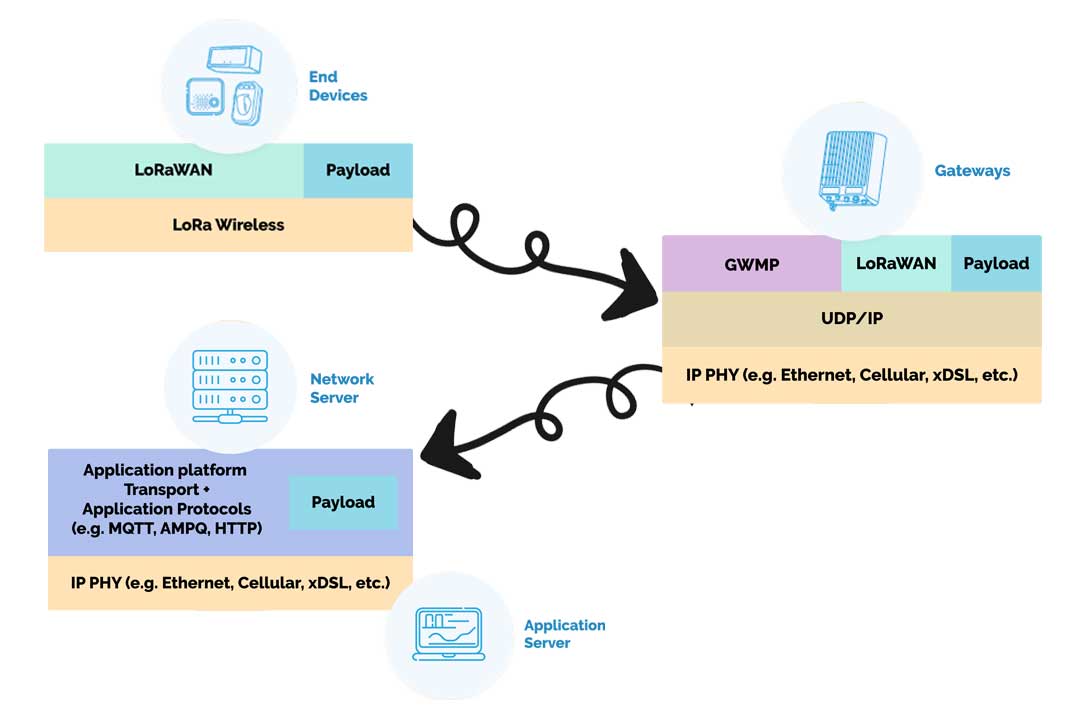
A LoRa™ network consists of three main components: the LoRa transmitter, the gateway, and the central server. The LoRa transmitter, embedded within the end device, collects sensor data and transmits it wirelessly over long distances using LoRa modulation. The gateway acts as a bridge, receiving data from multiple LoRa devices and forwarding it to the central server via a backhaul connection such as Ethernet, cellular, or Wi-Fi. The central server processes and manages the received data, ensuring secure and efficient communication between devices. The application server connects to the central server, retrieving sensor and device data for further analysis and integration into IoT applications.