TPMS Solutions
A Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) is an advanced technology designed to automatically monitor the condition of vehicle tires. TPMS continuously tracks tire pressure and, in some cases, temperature, using either direct sensors installed inside the tires or indirect methods based on wheel speed data.
By providing real-time alerts about low tire pressure or abnormal conditions, TPMS enhances driving safety, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity. This system helps prevent accidents caused by underinflated tires, improves vehicle handling, and reduces carbon emissions by maintaining optimal tire pressure.
A TPMS typically operates using either direct sensors installed inside the tires, which measure actual air pressure and transmit real-time data to the vehicle’s monitoring system, or indirect methods that analyze wheel speed variations through the ABS system to estimate changes in tire pressure based on rotational differences. Here, we provide a brief overview of both TPMS methods.
Indirect Type of TPMS
An Indirect Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) does not measure actual tire pressure but instead estimates it using data from the wheel speed sensors of the vehicle’s Anti-lock Braking System (ABS).
Each tire’s diameter slightly decreases when its pressure drops, causing the affected wheel to rotate at a slightly different speed compared to properly inflated tires. The ABS system continuously monitors these rotational speeds and detects discrepancies that may indicate underinflation.
Additionally, the ABS determines whether a wheel is locked or slipping based on wheel speed sensor data. If a wheel is rotating too slowly compared to others during braking, the system activates the anti-lock braking function to prevent skidding. In indirect TPMS, similar principles are used to analyze speed variations and infer tire pressure changes.
Direct Type of TPMS
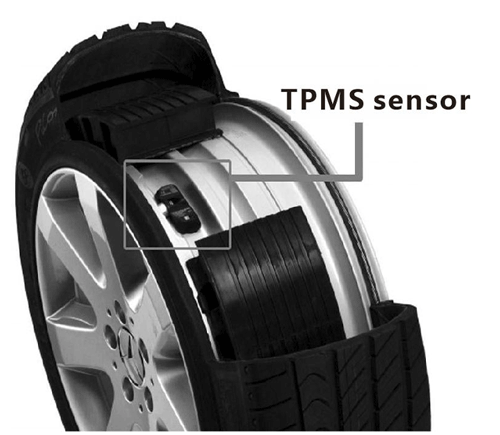
Here, a sensor installed in each tire directly measures the tire pressure and transmits the data wirelessly to a central receiver module. The system then displays real-time tire pressure and temperature information. If the tire pressure drops to an abnormal level, the system automatically triggers an alert to notify the driver.

The direct TPMS offers a higher level of functionality by providing real-time measurements of the actual air pressure inside each tire. This allows for easy identification of any faulty tire.
On the other hand, the indirect TPMS is relatively more cost-effective. Vehicles equipped with ABS (one wheel speed sensor per tire) only need a software upgrade to enable this system. However, the indirect system has lower accuracy compared to the direct system. It cannot pinpoint a specific faulty tire, and its calibration can be quite complex. In some cases, it may fail to function properly, especially when the air pressure of two tires on the same axle is low. Table below listed a comparisons between direct and indirect types of TPMS:
| Type Contrast | Indirect Type | Direct Type |
|---|---|---|
| Greater than 100Km/h | Unable to detect | Testable |
| Ipsilateral lack of gas | Unable to detect | Testable |
| [i+] false alarm | Often appear | not have |
| air pressure display | not have | have |
| Tire temperature display | not have | have |
| self checking function | not have | have |
| Technical difficulty | lower | Higher |

Share This Post:
Explore More
Leave a Comment
The Working Principle of Vehicle TPMS
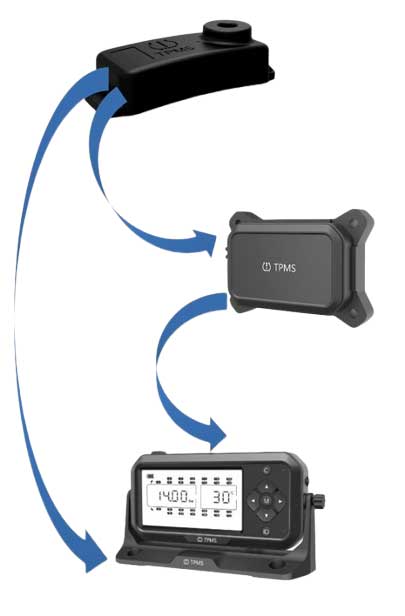
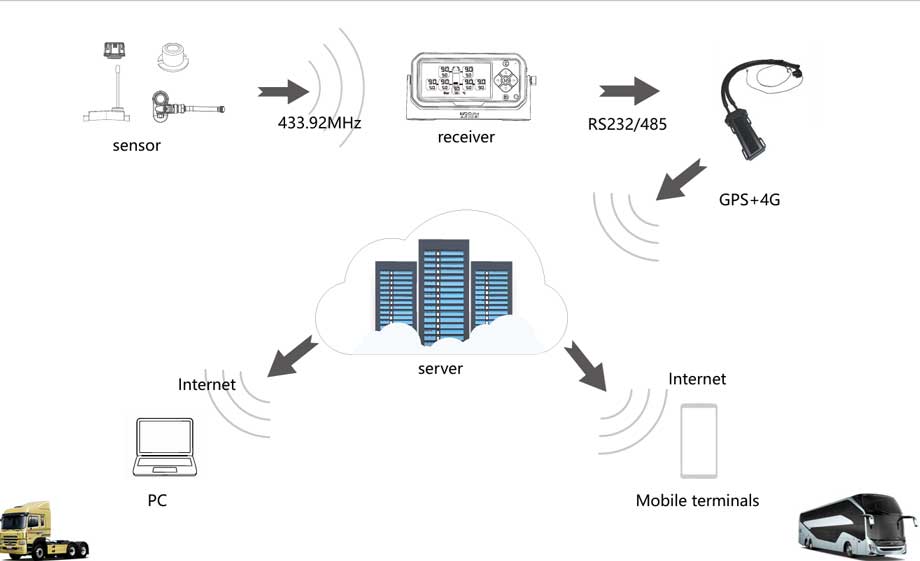
1. TPMS Sensor
The TPMS sensor measures tire pressure and temperature, then transmits the data wirelessly via RF signals.
2. Repeater
The repeater receives the signal from the TPMS sensor, amplifies the power, and retransmits it via RF. (For vehicles with more than 22 wheels, two repeaters are required.)
3. Receiver & Display Unit
The receiver collects signals from both the TPMS sensor and repeater, processes the tire data, and displays the information. If an abnormality is detected, the system immediately triggers an alert.
Sensor Categories for Large Vehicles

External Type
Drawbacks: Limited temperature accuracy, incompatible with special valve nozzle diameters, and operates only down to -30°C.

Standard Internal Type
✅ Advantages: Accurately measures air pressure and temperature without affecting the vehicle’s appearance.
❌ Disadvantages: Higher installation costs, compatible only with vacuum tires, and requires a standard valve nozzle diameter.

Internal Type
✅ Advantages: Accurately measures air pressure and temperature, does not affect the vehicle’s appearance, and has no impact on the original tire.
❌ Disadvantages: Higher installation costs and compatible only with vacuum tires.