NB-IoT Network
Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) is a wireless communication technology standardized by 3GPP and recognized as one of the leading emerging LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) solutions. Designed to connect a wide range of IoT devices, including smart parking systems, smart water and electricity meters, wearables, and industrial applications, NB-IoT was first introduced in 3GPP Release 13 (NB1) for low-power, stationary devices.
NB-IoT operates on an ultra-narrow bandwidth of 180 kHz, reducing hardware costs and power consumption. However, with the enhanced 3GPP Release 14 (NB2), it supports improved mobility and higher data rates:
- NB1 (Rel 13): Up to 21 kbps download and 62.5 kbps upload.
- NB2 (Rel 14): Up to 120 kbps download and 160 kbps upload.
With its low power consumption, extensive coverage, and cost-effective deployment, NB-IoT is positioned as a key technology shaping the future of the Internet of Things.
The NB-IoT network is a low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) technology standardized by 3GPP, specifically developed for IoT solutions. As one of the latest LPWAN options introduced after the emergence of LoRaWAN and Sigfox, NB-IoT aims to provide an energy-efficient and cost-effective communication protocol. It operates in licensed frequency bands, ensuring reliable connectivity under the management of mobile network operators.
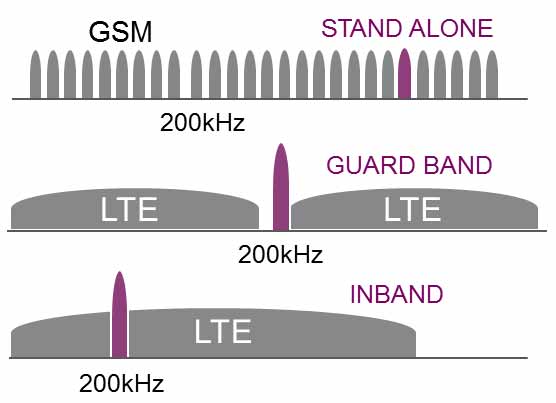
This technology is not dependent on traditional LTE infrastructure and can be deployed in three different modes:
- Standalone: Operates on a dedicated spectrum independently.
- In-band: Runs within the resource blocks of a standard LTE carrier.
- Guard-band: Utilizes unused resources in the guard band of an LTE carrier.
Communication Challenges in IoT Devices
IoT devices need to be designed to send data 24/7 and keep users updated. This continuous data transmission increases power consumption, which in turn leads to higher bandwidth requirements, reduced battery life, and increased communication costs in LTE networks.
Benefits of NB-IoT
As a low-power, cost-effective communication technology, NB-IoT addresses these challenges and offers the following benefits:
- Strong Signal Penetration: NB-IoT is designed to ensure its signals can pass through multiple layers of concrete and physical obstacles, providing better coverage than other technologies.
- Low Power Consumption: NB-IoT devices do not require heavy operating systems like Linux, making them much more energy-efficient compared to other communication technologies.
- Cost-Effective: The simpler hardware complexity in NB-IoT significantly reduces the cost of manufacturing and deploying devices.
- Long Battery Life: The electronics in NB-IoT devices consume very little power, allowing them to operate for up to 10 years without battery replacement.
- High Security: NB-IoT offers a high level of security through data encryption, secure authentication, and signal protection.
Other Benefits of NB-IoT
- High Penetration in Underground and Urban Areas: Compared to GSM modems, NB-IoT offers superior signal penetration in challenging environments such as underground or densely built urban areas.
- Wide Connectivity Capability: NB-IoT supports a vast number of IoT devices, making it ideal for connecting billions of devices.
- Low Deployment Costs: The cost of setting up an NB-IoT network is significantly lower compared to traditional communication networks.
- Plug and Play Capability: NB-IoT devices are easy to deploy with minimal setup, requiring no complex configurations.
- Suitable for Various Environments and Applications: NB-IoT is versatile and adaptable, making it suitable for a wide range of environments and use cases.
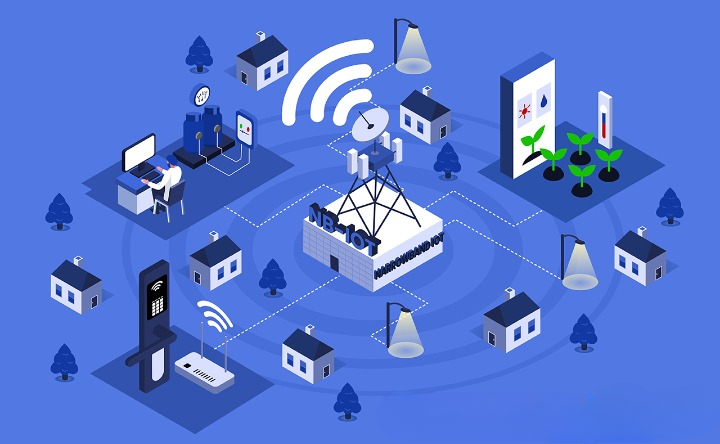
NB-IoT Applications
- Smart Metering: Enables monitoring of water, electricity, and gas meters in remote and underground locations with weak network coverage.
- Energy Management: Uses NB-IoT sensors in buildings to optimize energy consumption.
- Water Resource Protection: Controls water usage in buildings through NB-IoT sensors.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): Tracks inventory, customer data, and product distribution.
- Temperature Monitoring & Store Layout Optimization: Maintains optimal conditions for perishable goods and enhances store arrangements.
- Smart Cities: Facilitates street lighting control, waste management, environmental monitoring, and traffic control.
- Smart Buildings: Monitors indoor conditions, manages security alerts, and maintains optimal temperature settings.
- Tracking: Provides location tracking for people, animals, and valuable assets, especially in cases where continuous connectivity is not required.
- Smart Agriculture: Monitors soil temperature and humidity, detects environmental changes, and alerts farmers in case of anomalies.
How to Connect to an NB-IoT Network?
To use NB-IoT, specialized modules supporting this technology are required. Standard GSM modems do not support NB-IoT. Fortunately, in the Iranian market, the Quectel BC95 module is a viable option for implementing NB-IoT projects.